Quality Basics: QMS allows you to create Deviation records to help you track and manage deviations from your site’s established processes. The Deviation workflow allows for identifying process deviations, determining the severity of deviations, assessing their impact, investigating root causes, determining required actions, and capturing QA approvals.
The Deviation workflows in Quality Basics: QMS differ depending on whether the Deviation is Minor, Major, or Critical.
About Minor Deviations
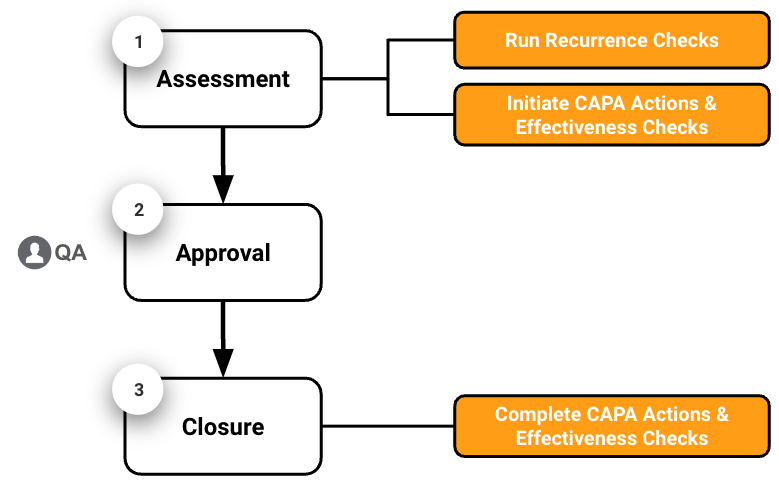
Quality Basics: QMS provides the tools you need to manage Minor Deviations in three (3) main stages: assessment, approval, and closure.
- Assessment: The Deviation Owner reviews the Deviation record and runs a Recurrence Check to determine if the deviation has occurred before. Then, the Deviation Owner determines the root cause, completes the Impact & Risk Analysis, completes the Investigation, creates CAPA Actions, creates Effectiveness Checks, and creates Extension Requests as needed.
- Approval: The QA Approver reviews the Deviation details and related records and approves the Deviation, which closes it.
- Closure: Once the Deviation is closed, the CAPA Actions and Effectiveness Checks Owners complete their respective actions and checks.
About Major & Critical Deviations
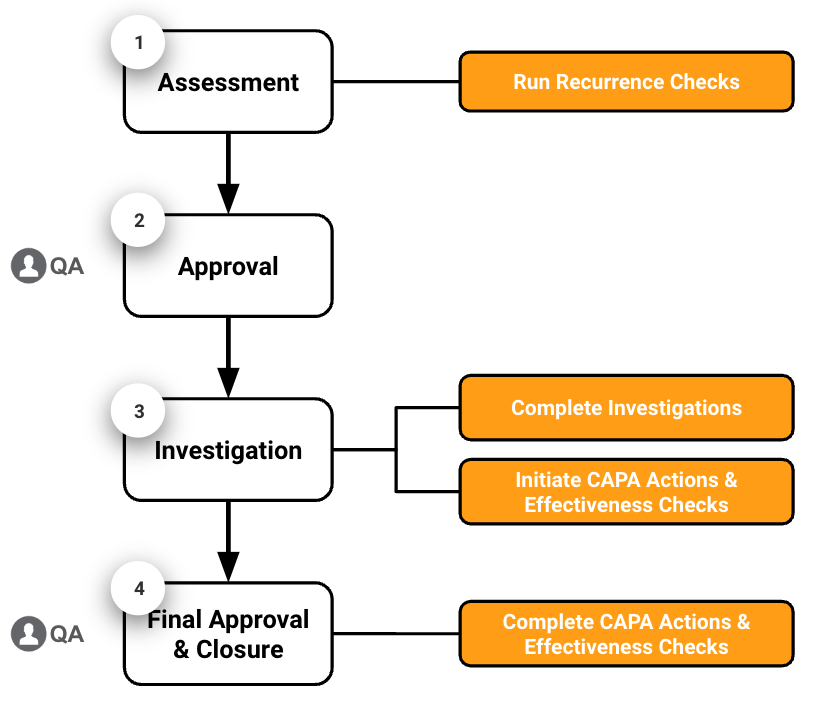
Quality Basics: QMS provides the tools you need to manage Major and Critical Deviations in four (4) main stages: assessment, approval, investigation, and final approval & closure.
- Assessment: The Deviation Owner reviews the Deviation record, runs a Recurrence Check to determine if the deviation has occurred before, and creates Extension Requests as needed.
- Approval: The Deviation Owner sends the Deviation to the QA Approver for approval. The QA Approver reviews and approves the Deviation.
- Investigation: The Deviation Owner determines the root cause, completes the Impact & Risk Analysis, completes the Investigation, creates CAPA Actions, creates Effectiveness Checks, and creates Extension Requests as needed.
- Final Approval & Closure: The QA Approver reviews the Deviation details and related records and approves the Deviation, which closes it. The CAPA Actions and Effectiveness Checks Owners complete their respective actions and checks.
About Deviation Teams
When you create a Deviation, you are prompted to select the team members responsible for it. Records created from a Deviation, such as Impact Assessments, Investigations, CAPA Actions, and Effectiveness Checks, also require you to select the responsible team members.
When you first create a record that requires a team, a team required icon () is displayed in the left panel and the Team section heading. After adding and saving the team members, the icon is removed, and the record can progress to its next lifecycle stage.
The following team roles are available:
- Owner: The Owner assigned to a record is responsible for managing and performing the main actions or tasks associated with the record. For example, the Owner of a Deviation is responsible for reviewing the Deviation details, creating CAPA Actions and Effectiveness Checks, and investigating the root cause and impacts of the Deviation.
- QA Approver: The QA Approver assigned to a record is responsible for performing the quality review and approval. The QA Approver is typically a member of the Quality team. For example, the QA Approver is responsible for confirming that the outcome details in an Effectiveness Check were performed according to the Results information documented in the Effectiveness Check record.
When defining a team, you can select multiple QA Approvers. If you select multiple users for these roles, all selected users must select the Approve verdict for the record to be considered approved. If at least one approver selects the Reject verdict, the record is rejected and returned to the Owner.